The University of Maryland has calculated that every 39 seconds, there are hacker attacks on computers with Internet access. More than 120 countries have adopted international data protection laws to make the movement of data safe. One such law is the GDPR. What is it, who will have to implement it, and what is the essence of the GDPR - we will explain everything you need to know.
What is GDPR?
The GDPR is the general data protection regulation for European Union (EU) citizens. The law explains what personal data is and establishes the rules for its responsible management. Businesses that collect, process and store data to provide services to EU residents of the following countries will have to implement the GDPR:

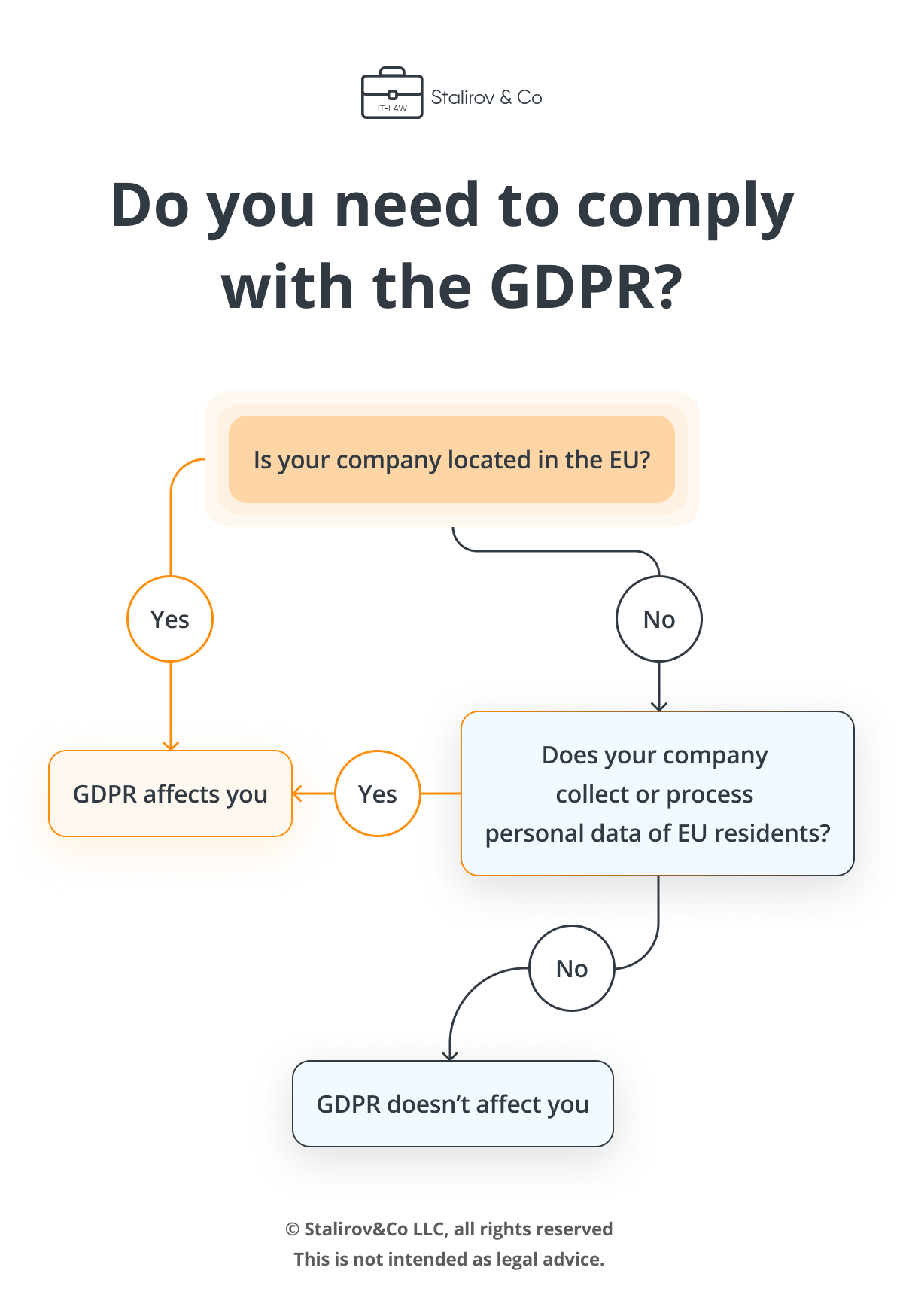
If your business is physically located in the EU, it needs to comply with the GDPR. Geographically, your company may be located in the United States or China, but if you sell goods, provide services, or hire EU citizens, then you are subject to European regulations. Please answer the questions below to find out if you need to implement the GDPR.
Personal data processing principles
The processing of personal data must be carried out following seven principles, which are enshrined in article 5 of the GDPR.
Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
The lawfulness, fairness, and transparency principle means that the organization receives data legally; fulfills its obligations to store and transfer data; provides comprehensive information about the collection, processing and storage.
One of the legal grounds for processing is the customer's consent. Each action with personal data must be coordinated with the customer.
Information about how the company processes data must be complete.
The requirement for completeness includes the prohibition of covert and invisible processing.
In addition to the completeness, the accessibility condition must be met.
Companies that publish Privacy Policies on websites and applications must describe the collection and processing processes in clear, concise, and straightforward language to make it easier for the user to understand how their data is processed. The owner of an IT product must highlight the most critical points in the document and provide information using different channels of interaction. For example, you can use video content, informational snippets, or pop-ups. In addition, the confidential policy must be placed in an accessible place. User habits demonstrate that the site footer or app dropdown is the ideal place to link to a policy. Thus, the user is always one or two clicks away from accessing the document.
Purpose limitation
The company must communicate to customers the purpose of data collection. They must be specific, distinct, and legal. Data may be collected and used only for purposes that are necessary for the provision of the services.
IT lawyers from Stalirov&Co developed the Privacy Policy for SmartWatch, a mobile application for synchronizing watches with an Android device. In the document, lawyers described the specific and legitimate purposes of collecting personal data: SmartWatch collects personal data to improve the service, communicate with visitors, and online sales. SmartWatch uses personal data to make the application work quickly and efficiently. The main purpose of data processing is to ensure that the use of the application will be convenient and understandable. In addition, the application uses data for other reasons, such as security, customer support, marketing, compliance with legal obligations, accounting requirements, and software development.
The more detailed the list of goals, the less likely it is that you will get a fine for violating GDPR principles.
Minimization
Collect the minimum necessary and mandatory data. Companies should limit the collection of personal information to what is directly relevant and necessary to accomplish a specified purpose. Let's take a look at an example. An online e-book store has placed a form on their site that the user must complete to place an order. The online store owner used a standard contact form, asking for the first and last name, date of birth, phone number, email and home address. But not all fields in a form are strictly required. To place an order for an ebook, you only need a first name, last name, and email to which the book text will be sent. The collection of other personal data violates the principle of minimization.
Access to data should be given only to those employees who need it to complete their work.
Accuracy
The principle of accuracy requires companies to keep only up-to-date data and update it if necessary. To fulfill the requirement you can verify the accuracy of the data by using an update query. An example of this is the Freedom Finance investment company. They annually ask brokerage account holders to submit an order to change information and attach relevant documents in the desktop and mobile versions of the Tradernet application. If the client does not do this, access to the account is blocked until the data is updated.
To meet the accuracy requirement, medical institutions are implementing a hashing method. There is a risk of error when two people receive the same treatment simultaneously, and the name is the only parameter that separates them. Therefore, a unique identifier is needed for each person. To do this, institutions create immutable hash signatures for the records of the treatment logs and the employee associated with the patient. Thanks to this, any changes in personal data can be recognized, compared and tracked.
Violation of the principle of accuracy leads to fines.
Storage limit
Companies need to establish a retention period for personal data and justify that this period is necessary for specific purposes.
Integrity and confidentiality
Companies need to implement technical solutions to protect data from unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction or damage. For example, if a company wants to transfer customers' personal information from the database to the server. The risk is that all employees have access to the server, but only one department needs to process the data. To regulate the access and reduce potential damage from malware, a company can partition the network and set up server access control.
In addition, you can implement security monitoring and install an intrusion detection and prevention system. Thanks to an automated audit system, violations of processing rules can be quickly and easily recognized.
Accountability
Each step of dealing with personal data should be described in detail in official documents:
- Privacy Policies
- Data protection agreements
- Data protection instructions for employees
- Procedures for responding to and reporting a leak and others.
The company must provide all these documents to the supervisory authorities to confirm data protection compliance. Otherwise, companies can get heavy fines.
What technical and organizational security measures should a company implement to be GDPR compliant?
A company needs to implement the following technical and organizational measures to ensure a high level of security:
- Pseudonymization and encryption.
- Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, availability and stability of processing systems and services.
- Prompt restoration of data availability.
- Regular testing of security measures.
Security system errors can lead to both minimal and million-dollar fines.
To ensure compliance with GDPR and improve data security, consider implementing these cybersecurity solutions:

How to pass GDPR compliance?
IT-lawyers of Stalirov&Co compiled a list of actions to satisfy the requirements of the regulation. So, to be GDPR compliant you need to:
- Conduct a GDPR audit to determine what personal data the company collects, on what grounds, and for what purpose. This will help implement the principle of legality.
- Develop GDPR documentation as required by the principle of accountability. Online stores, marketplaces, mobile applications, Gamedev products and other software solutions that collect personal data from users on the Internet will need a Privacy Policy. Companies from finance, medicine, insurance, tourism and other industries must implement internal agreements, policies and guidelines — for example, Data protection agreements with contractors and employees.
- Make regular updates to the GDPR documentation so that customers receive up-to-date information about the processing and storing of their data. Promptly update information at the request of data subjects. This will delete the principle of transparency and accuracy.
- Establish a data retention schedule to meet retention deadlines and comply with deletion requirements.
- Hire a Data protection officer who will help implement technical and organizational security measures and ensure compliance to GDPR processing requirements.







