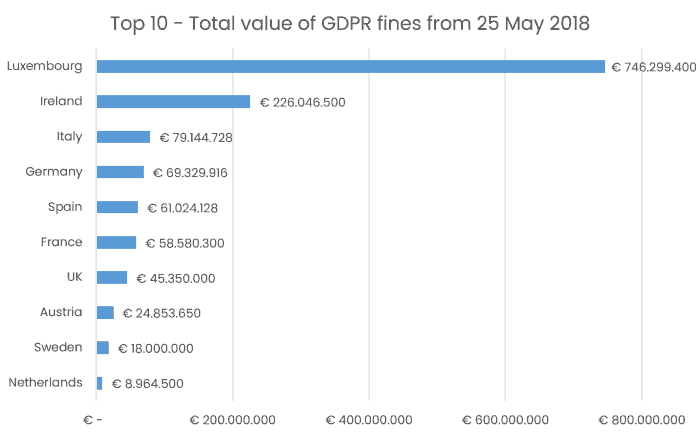
Data protection supervisory authorities across Europe have imposed nearly 1.1 billion EUR in fines since January 28, 2021.
The largest 746 million EUR fine was imposed on Amazon by the Luxembourg Supervisory Authority. Irish Data Protection Commission imposed a fine of EUR 225 million on WhatsApp. This is a 14-fold increase on the previous record fine imposed on Google by the French authorities last year.
In its report, DLA Piper’s cybersecurity and data protection team developed a fines ranking.
Many well-known US multinationals have offices in Luxembourg and Ireland. There are Amazon, Microsoft, PayPal, Oracle, Meta, Intel Corporation, LinkedIn, Apple, eBay etc.
Therefore, companies that process personal data of EU citizens must comply with the requirements of the GDPR, even if they are from the United States.
The business owner is responsible for choosing the partner who has access to the company's data. Imagine that you are hiring a company to build a CRM system for an international E-commerce platform. The development of such a solution assumes that IT specialists will have access to the client's personal data from all over the world, including the EU. Both you and the IT company must guarantee data safety. This rule is spelt out in the GDPR stipulating that both parties are responsible for processing.
To ensure data security, an IT outsourcing company needs to conduct internal audits and ensure a high level of cybersecurity. Companies should have a clearly defined privacy policy in place. And finally, they must be ready to sign the DPA (Data protection agreement). This article describes why the business needs a DPA and how to draw up an agreement.

What is a DPA?
DPA is a data processing agreement. The agreement helps companies to ensure that all data processing activities comply with the GDPR policy. By signing the document, both parties protect the project data and receive a strategy for preventing and eliminating data leakage.
Who needs to sign the DPA?
There are three scenarios for working with external contractors.
1. No personal data processing occurs. For example, an IT company conducts UX/UI research and develops a prototype app for a bank. Such an executor doesn't get access to the personal data of bank customers, which means that DPA is not needed.
2. Personal data processing occurs, but data access is limited. The IT company team has access to the databases in an unreadable encrypted form, so in this case, there is no need to sign the DPA.
3. The provider processes data on behalf of the controller. For example, an IT outsourcing company receives an order from a client to develop an application for data management in a healthcare facility. They need access to patients' personal information. In this case, it is mandatory to sign the DPA. In addition, before the start of work on the project, the company needs to adapt in-house processes to the requirements of the agreement and pass the GDPR Compliance.
What to write in the DPA?
Section 3 Article 28 of the GDPR establishes a list of must-to-include provisions for DPA. We will describe further the details using sample agreement between a customer (controller) and an IT company (processor).
- Processing based on written instructions from the controller
The processor may only process personal data following the controller's documented instructions.
In April 2022, CHIL imposed a EUR 1,500,000 fine on DEDALUS BIOLOGY. The company has developed IT solutions for laboratory management. 3,000 private and 30 public laboratories have purchased software licenses. In 2021, the personal data of 491,840 patients leaked and were sold on the dark web. During the review, CHIL found that DEDALUS BIOLOGY extracted more information than required and processed the data in violation of the instructions.
Such situations lead to millions in fines. Therefore, GDPR documents must include a detailed description of processing scope and security measures.
- Everyone who has data access is liable for the violation of instructions
The processor grants access to personal data only to those team members who have undertaken to maintain confidentiality. In addition, the team needs to be trained regularly and conclude a DPA with each of them.
- Involvement of a subprocessor is possible after agreement with the controller
Permission to attract new employees or contractors must be in writing. It is essential to spell out in DPA the conditions for attracting subprocessors.
An IT company may transfer the processing of personal data, provided that:
- attracts sub-processors on its behalf under a written agreement but informs the customer about additions and replacements in the team;
- a company is responsible for sub-processors violations;
- evaluates the sub-processor's security and privacy practices to determine that it is capable of providing the high level of personal data protection required by the DPA;
- publishes a team roster or provides information upon request.
The customer may object to changes in the composition of the team and report this within a certain period. But the DPA should have a clause about force majeure replacement. The IT company may replace the sub-processor without prior notice if it needs to act immediately. For example, a developer quits.
Engaging contractors without the permission of the controller may result in a fine. So in May 2022, Wens Experience SRL paid 1,500 EUR for involving an employee in data processing without written permission, which means that it violated Article 28 of the GDPR.
- Implementation of the security measures under Article 32 of the GDPR
Here is a list of security measures: anonymization and encryption; ensuring the continued confidentiality, integrity, availability and resilience of processing systems and services; timely data access resumption and testing the effectiveness of measures. Before starting work on the project, the IT company must implement such measures.
In the DEDALUS BIOLOGY case, the company also paid a fine of 1,500,000 EUR because it violated Article 32 of the GDPR. CHIL found that the company did not have a procedure for transferring data. There wasn't encryption and the automatic deletion of data after a transfer. As well as there wasn't authentication for accessing the public area of the FTP server.
- Assisting the controller
For example, the processor will cooperate with the controller when considering requests from data subjects or regulators.
- Deleting data
The client may instruct to export, extract or delete personal data remaining on the servers.
- Providing information to demonstrate compliance
The client or its auditor may review the security environment and practices. In DPA, we advise you to detail the algorithm and timing of the audit. For example, the controller gives 60 days notice of an audit via email. The frequency of inspections cannot exceed more than once a year. Audit time is limited to three working days. The parties may agree that the verification is carried out online. And don't forget to identify who bears the cost of the audit.
Now let's take a closer look at the structure of the document.
Stalirov&Co IT lawyers develop DPA in the format of the main agreement and annexes, which define the subject, types and purpose of personal data processing, categories of data subjects, technical, and organizational measures. Let's talk about each section in more detail.
Subject and categories of personal data
If an IT company develops software for online banking, then the data subjects will be the bank's customers. Then developers get access to the following types of data: name, phone numbers, email addresses, time zone, address data, system access/usage/authorization data, contract data, financial and bank details, and credit card numbers.
For each case, the list will be different.
Processing purposes
The list of targets might look like this:
● use of personal data to configure, operate, monitor and ensure the functionality of the software product;
● communication with data subjects;
● storage of personal data in data centres;
● updating the software product;
● backup of personal data;
● computer processing of personal data, including transmission, search and access;
● access to the network for data transfer.
Technical and organizational measures
For the DPA of an outsourcing IT company, Stalirov&Co IT lawyers suggest the following list of measures.
● Physical access control prevents unauthorized access to the premises where data processing systems are located. For example, buildings and offices are secured with a smart card access system. The extreme points of entry into the building must be equipped with a certified key system. Special access profiles, video surveillance, intruder alarm systems and biometric access control systems should protect individual areas. Physical security equipment (motion sensors, cameras) is regularly tested. Guests and visitors to the buildings must register at the front desk.
● Access control and management system. When granting access to confidential systems, several levels of authorization are used. All personnel get access to systems with a unique identifier. When an employee leaves the company, their access rights are revoked. All passwords must meet minimum requirements and be stored encrypted. The exchange of passwords is prohibited, and the system requires regular changes. Firewalls protect the company network from the public network. The company uses up-to-date anti-virus software at network access points on all file servers and workstations. Sophisticated authentication protects remote access to the corporate network and critical infrastructure.
● Data access control. IT professionals only get access to the data they are entitled to. However, the data may not be read, copied, modified or deleted without permission. The team has access to the information that is necessary to complete the tasks. The IT company uses authorization concepts that document the provisioning processes and assigned roles for each account. Installation of unapproved software is prohibited.
● Data transfer control. The movement of data must be protected.
● Data entry control is the ability to retrospectively check and establish whether data has been entered, modified, or deleted from processing systems, and by whom.
● Availability control. Personal data must be protected from accidental destruction or loss. To achieve this goal, the company uses regular backup processes and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS, batteries, generators). Emergency processes and systems are regularly tested.
● Data integrity control. The company implements a multi-level strategy for protection against modifications. Uses firewalls, and anti-virus software and conducts external and internal penetration testing.
Standard Contractual Clauses
SCC must be signed if the data is exported outside the European Economic Area, to countries with no sufficient level of security.
You don't need to develop SCC by yourself. Just sign the standardized document already developed by the European Commission. This action is provided for in Article 46 of the GDPR. However, not everyone follows this rule.
The French construction company Futura International was imposed a fine of EUR 500,000 in 2019. The company transferred data to Côte d'Ivoire, Morocco, and Tunisia via Profibus software. There was a contract between Futura Internationale and the contractor, but it didn't include all the necessary conditions for cross-border data transfer. It is because Futura International decided to develop its agreement and didn't use SCC.
How can you transfer data from the EU to the USA?
EU and US companies had been free to transfer data to each other based on the Safe Harbor. But then, Austrian data protection activist Max Schrems complained that the US as a country wasn't providing sufficient protection for the personal data of EU citizens. After that, the European Court of Justice (CJEU) ruled in favour of the activist and annulled Safe Harbor.
In 2016, the US and the EU signed the Privacy Shield. However, Max Schrems appealed the act again, and the CJEU annulled the Privacy Shield.
On March 25, 2022, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and US President Joe Biden announced an agreement on personal data transfer from the EU to the US. The Trans-Atlantic Data Privacy Framework is expected to be ready by the end of the year.
Until the act is adopted, data transfer from the EU to the US is carried out according to Standard Contractual Clauses.
Who will pay the penalty for violating the GDPR: the controller or the processor?
Companies must remember that when outsourcing data processing to contractors, they are considered controllers and responsible not only for their GDPR compliance but also for compliance with the rules by processors.
It is impossible to shift responsibility to the processor. But many companies have tried. For example, in 2020, British Airways and Marriott claimed that third-party service providers, rather than them, were to blame for the data breach. But the argument wasn't taken into account. Each company had to pay fines of more than EUR 20 million.
On the other hand, the processor is liable for GDPR non-compliance or going beyond the instructions from the controller. This rule is spelt out in Article 82 of the GDPR. For example, DEDALUS BIOLOGY was the processor but paid a fine of EUR 1,500,000 for extracting more information than the instructions required.
The controller and the processor can protect themselves against unfair penalties if the DPA between them describes the objects and purposes of processing and organizational and technical security measures in detail.





