Imagine this: You're building a successful business, expanding into new markets, and scaling up. But one mistake, and you're slapped with a $100 million fine. This is exactly what happened to the crypto exchange BitMEX, which ignored AML (Anti-Money Laundering) requirements. U.S. authorities concluded that the company failed to properly vet its clients, resulting in heavy penalties.
To avoid such a scenario, it's crucial to establish a proper AML screening process. We've prepared a simple guide to help your business meet legal requirements and efficiently conduct AML checks.
What is an AML check?
An AML check is a procedure designed to detect suspicious financial activities and prevent money laundering. Companies conduct these checks to ensure their clients or partners are not involved in illegal activities such as financing terrorism, corruption, or tax evasion.
AML verification plays a key role in ensuring these checks are accurate, thorough, and compliant with financial regulations. Without proper verification, businesses risk failing to identify high-risk clients or suspicious activities.
Who needs to conduct AML checks?
AML procedures are mandatory for companies dealing with financial transactions that could potentially be exploited for illegal activities. These include:
- Banks and financial institutions – credit organizations, payment systems, and investment firms.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges and services – exchange platforms, wallets, and DeFi projects.
- Fintech companies – e-wallets, P2P lending services, and payment gateways.
- Brokers and investment funds – companies dealing with securities, stocks, and derivatives.
- Gambling and betting platforms – online casinos, betting websites, and lotteries.
How does the AML check work?
An AML check starts with thorough preparation, including gathering information, training staff, and implementing policies.
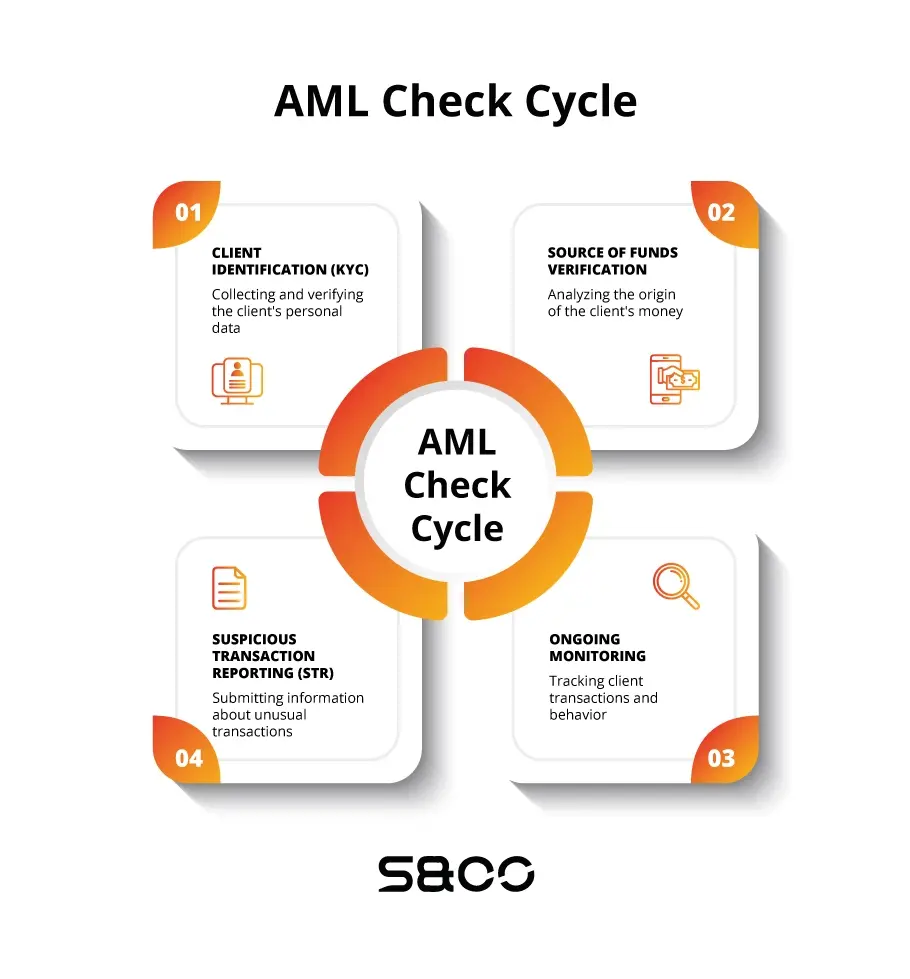
In the initial stage, risks are assessed using KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures. This involves verifying and screening clients.
When a client opens an account, the company must request:
- Identification details (full name, date of birth, address).
- Identity verification documents (passport, driver's license).
- Business information for corporate clients (company name, type, and industry).
- Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) details.
- Source of funds or asset ownership documents.
Once the client’s identity is verified, the financial institution evaluates potential risks by analyzing the client’s financial history, industry, and business connections. Companies also check clients against watchlists, including:
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEP).
- Special Interest Persons/Entities (SIP/SIE).
- Relatives and Close Associates (RCA).
- Terrorist watchlists.
Additionally, companies analyze previous transactions, credit history, and geographical locations. Performing an AML search helps organizations track any links to suspicious financial activities, improving their ability to identify and mitigate risks.
For corporate clients, a more detailed examination is required, including reviewing executive backgrounds and financial reports. This helps assess risk and predict future actions.
These steps must be conducted regularly to maintain compliance and protect the financial system from illegal activities.
Best practices for effective AML checks
To enhance the AML check process, we recommend that financial institutions:
- Use reliable data sources for up-to-date information.
- Maintain detailed client profiles using encrypted databases and secure cloud systems to ensure GDPR/CCPA compliance.
- Segment clients by risk profile so that high-risk clients undergo enhanced due diligence (EDD).
- Regularly update client information, especially for high-risk individuals or those with changing business activities.
- Implement automated identity verification tools to reduce errors and speed up customer onboarding.
- Automate monitoring systems to track changes in client status.
- Set threshold limits for high-risk clients, such as large transfers or transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions.
- Monitor international sanction lists like OFAC (U.S.), UN Sanctions, and others to oversee cross-border transactions.
Many companies use AI-driven fraud detection systems to monitor high-risk transactions quickly and accurately.
Anti-money laundering checks by banks are particularly stringent, requiring banks to adhere to both national and international financial regulations. Banks must implement advanced AML strategies to detect illicit financial activities efficiently.
AML check for crypto wallets
Crypto exchanges are increasingly strengthening their AML checks. In addition to standard control criteria, crypto wallet checks involve:
- Identifying links to known ‘dirty’ wallets (e.g., those tied to darknet activities, sanctions, or hacks).
- Detecting suspicious transactions, including:
- Use of mixers like Tornado Cash or Wasabi Wallet.
- Chain transactions (peel chain).
- Unexpected large transfers or frequent small transactions.
- Identifying involvement in scams or phishing attacks.
- Tracking the 'cleaning' of funds via decentralized exchanges (DEX) or cross-chain swaps.
What to do if suspicious activity is found?
If suspicious activity is identified, the company must report it to the appropriate financial crime agency. Different countries have their own authorities:
- U.S.: FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network)
- UK: NCA (National Crime Agency)
- Canada: FINTRAC (Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada)
- EU: Europol
- Ukraine: State Financial Monitoring Service of Ukraine
Short checklist for successful AML checks
To ensure your business follows legal standards, prevents illegal financial activities, and avoids penalties, implement these steps:
- Develop AML policies and train employees.
- Collect client data.
- Conduct KYC procedures.
- Assess client risks.
- Conduct Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients.
Following these steps will help your company stay compliant, safeguard against illicit financial activities, and avoid costly fines.






