Interest in the cryptocurrency market continues to surge, with venture capital investment in digital-asset companies rising to $19.7 billion in 2025, according to PitchBook. Before these companies can secure investors and successfully launch their products, they must first determine the best jurisdiction for registering their business and acquiring the necessary cryptocurrency licenses. Let’s explore various regions, such as the US, Europe, and Asia, to discover which locations offer the most favorable options.
This article is aimed at those who are choosing the ideal country to establish their first cryptocurrency venture or are thinking about expanding into global markets.
What criteria should you use to choose the best country to register a crypto company?
By 2026, the crypto market has entered a phase of regulatory normalization, where enforcement, supervisory audits, and cross-border cooperation between regulators have become the norm rather than the exception.
Authorities are imposing hefty fines on crypto companies that operate without proper registration. In October 2025, Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) fined 19 companies for operating without the required licenses and breaching local marketing rules. Penalties ranged from AED 100,000 to AED 600,000 ($27,000–$163,000) per company. Beyond financial fines, VARA issued cease-and-desist orders, requiring the firms to immediately halt all promotional and business activities in Dubai. This enforcement action shows that even in crypto-friendly jurisdictions, compliance with licensing and advertising rules is no longer optional.
Fines for breaches of anti-money laundering (AML) regulations are becoming increasingly common. In January 2025, the US authorities fined BitMEX $100 million for violating AML requirements under the Bank Secrecy Act. Regulators found that the exchange had failed to implement an effective AML program and knowingly allowed users to trade anonymously, despite offering services to US customers.
To avoid fines, it’s crucial for crypto companies to choose countries with favorable conditions and comply with their regulatory requirements from the start. When the lawyers at Stalirov&Co advise crypto startups, they consider nine key criteria that can significantly impact a business:
- Capital requirements. These vary greatly between countries. For example, under the EU’s MiCA regime, capital requirements range from €125,000 to €150,000, depending on the type of crypto services provided. In the UAE, VARA requires share capital of AED 500,000–1,500,000, along with additional liquidity and reserve asset requirements.
- Regulatory requirements. This includes the need for a local office, the citizenship of directors, and audit requirements.
- AML compliance and KYC. The regulations should be carefully considered, including the obligations for AML officers and reporting.
- Taxes. Look at both general tax rates and special tax regimes for crypto companies.
- Country reputation. This is crucial for attracting investors or working with partners from other countries.
- Licensing. Analyzing licensing criteria is essential for ensuring legal compliance, gaining market credibility, managing costs, and securing long-term sustainability.
- Speed and ease of cryptocurrency company registration. Some countries offer faster and less bureaucratic registration processes.
- Access to banking services. This is especially important as many traditional banks are still cautious about working with crypto companies, which can complicate opening corporate accounts.
- Regulatory trends and future changes. It's crucial to account not only for existing regulations but also for any potential future changes that could affect your company’s outlook in both the near and distant future.
- Cybersecurity and tech audit. Regulators now mandate strict digital resilience standards, such as the EU’s DORA. Startups must undergo technical audits, including penetration testing, smart contract security reviews, and proof of robust custody architecture to secure a license in 2026.
Regulators assess not only licensing documentation but also how companies manage users after launch. We supported a public fintech company Intellabridge through a full legal and compliance review of its subscriber maintenance processes, including user data handling, access controls, and service continuity. This type of post-licensing scrutiny is now common during supervisory audits in the EU and the US.
Crypto companies in the US
If a crypto company wants to offer financial services to US citizens or operate within the US, it needs to obtain the proper licenses.
In early 2025, enforcement trends continued to highlight the importance of compliance. For example, BitMEX was fined $100 million for violations of U.S. anti-money laundering (AML) laws, after regulators found that the exchange had failed to implement an effective AML program under the Bank Secrecy Act and had allowed US customers to trade anonymously.
By late 2025, U.S. regulators began to reduce reliance on high-profile enforcement cases and shifted focus toward formal rulemaking and legislative clarification. While regulatory complexity remains, this marked a transition away from ad-hoc enforcement toward more predictable compliance expectations at the federal level.
Once you’ve considered and planned for these risks, we can dive into how to register a company and obtain a license in the US.
Crypto companies in the US are regulated on two levels:
Federal level
For AML/CFT purposes, companies engaged in crypto-related money transmission or exchange activities must register as a Money Services Business (MSB) with FinCEN. In addition to registration, companies must maintain a risk-based AML program, comply with applicable Travel Rule obligations, and meet enhanced transaction reporting expectations.
Steps to register as an MSB on the federal level:
- Get access to the BSA E-Filing System.
- Create an account.
- Complete FinCEN Form 107, disclosing the company’s legal structure, ownership and control persons, business activities, and designated AML compliance officer.
- Implement a written AML program aligned with US regulatory requirements.
- Receive crypto company registration confirmation from FinCEN.
State level
After registering as an MSB, companies must obtain a Money Transmitter License (MTL) in each state where they provide money transmission or crypto-related payment services.
Every state has its own specific criteria for issuing this license. If you want to offer your services throughout the entire US, you must obtain a Money Transmitter License (MTL),which covers the required crypto exchange license, from each individual state. Certain states have adjusted their licensing requirements or introduced new crypto-specific frameworks.
The expense of obtaining a license differs from state to state and includes the following fees:
- Application fees: The cost varies by state. For example, Texas charges $10,000, California charges $5,000, and Delaware charges $403.
- License renewal fees: California charges $2,500, and Delaware charges $230.
- Surety bond: Crypto companies must secure a surety bond to guarantee financial obligations. The business typically pays a percentage (1% to 3%) of the total bond amount. For instance, in Colorado the bond requirement is $1,000,000.
Crypto companies in Europe
Key advantages and challenges for crypto companies in the EU include:
- Unified regulation. The EU has a single regulatory framework for all member states, making it easier to operate within the internal market.
- High standards. The EU is recognized for its stringent requirements regarding AML, KYC, and data protection (GDPR), which can drive up compliance expenses.
- Access to banking services. In most EU countries, crypto companies have relatively easy access to banking services.
On April 20, 2023, the European Union approved the MiCA (Markets in Crypto Assets) regulation, which became applicable across the EU in December 2024. This established a unified framework for obtaining a crypto license in Europe, requiring all companies dealing with crypto assets in the EU to obtain a CASP (Crypto-Asset Service Provider) license to provide services. Under MiCA, a company qualifies as a CASP if it:
Holds and administers crypto assets for third parties
- Runs a trading platform for crypto assets
- Exchanges crypto assets for fiat currency
- Exchanges between two different crypto assets
- Issues crypto assets
- Accepts, transmits, and executes orders for crypto assets on behalf of third parties
- Provides advice on crypto assets
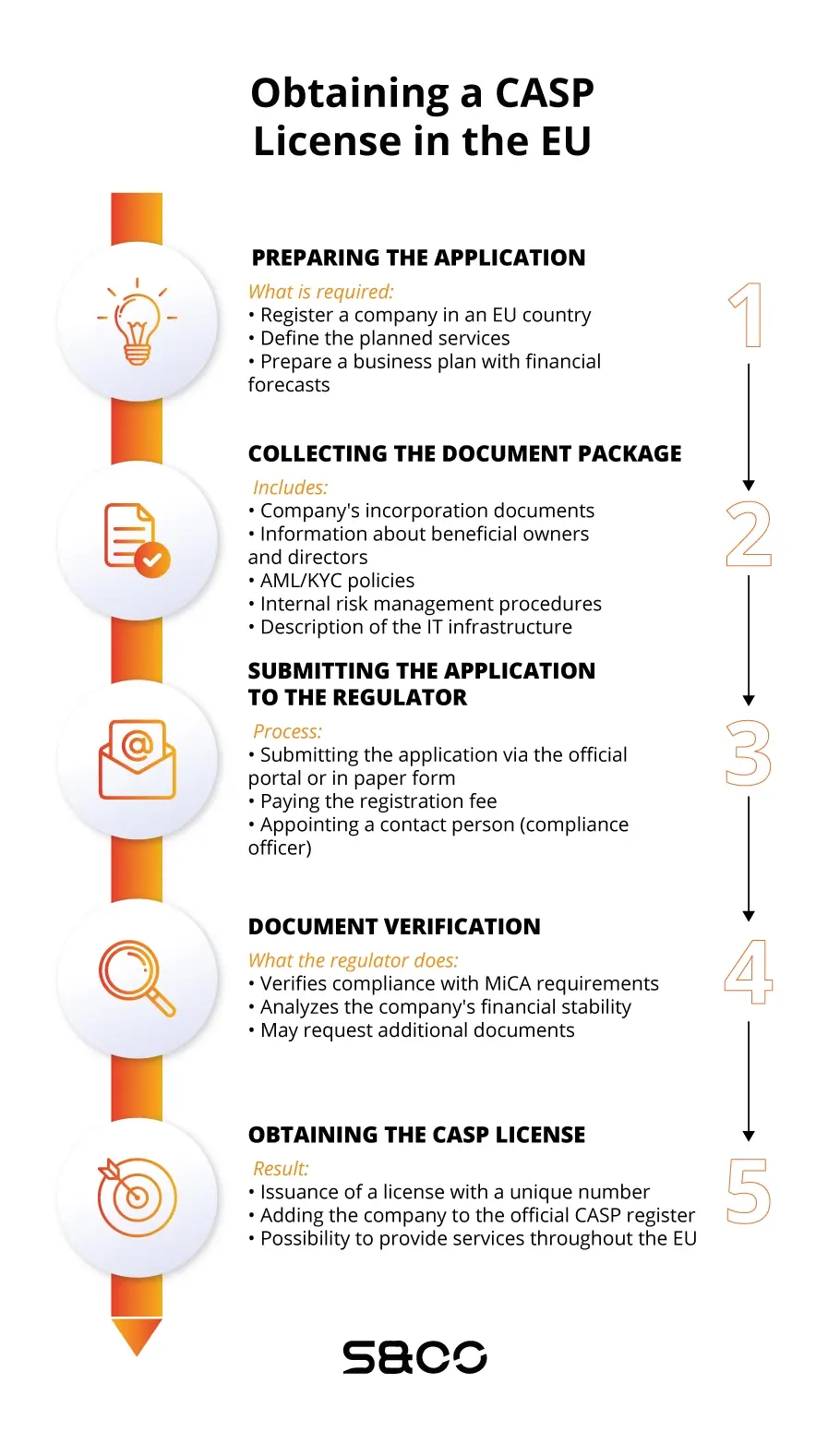
Under MiCA, all businesses operating with a Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) license will need to switch to the new CASP licensing system. To help them make the change, MiCA offers a transition period so these companies can adjust and get the CASP license they need.
The length and conditions of these transitional periods vary by country. For example, in Malta, the transitional rules allow virtual financial asset service providers who already had a license by December 30, 2024, to continue operating until July 1, 2026, or until their CASP application is approved or rejected, whichever occurs first.
Beyond transitional rules, several EU regulators have also moved to active enforcement of the new MiCA regime. In 2025, the French financial regulator (AMF) launched an enforcement campaign targeting crypto firms registered under the national PSAN regime. Registered providers were formally instructed to transition to full MiCA authorization or exit the French market by July 2026.
Alongside this, the AMF intensified supervision and continued adding non-compliant platforms to its public blacklist, while warning that MiCA allows fines of up to 12.5% of annual turnover for serious violations. The case illustrates how France is actively replacing registration-based crypto oversight with a strict authorization and enforcement model.
Against this regulatory backdrop, let’s explore one of the most popular EU countries to run the crypto startup.
Poland
Poland has become a leading hub for digital asset companies in the EU. Among the 2,000 crypto companies registered across 27 EU nations, nearly half are located in Poland. Before MiCA, crypto activities in Poland didn’t require a license, making things much easier.
Now, under MiCA, these rules have changed, and businesses are formally required to comply with the new licensing and regulatory requirements. However, the practical implementation of MiCA in Poland has been affected by developments at the national level.
Polish companies listed in the Polish VASP Register by December 30, 2024, were originally allowed to continue operating under the existing AML regime until June 30, 2025. In December 2025, the Polish President vetoed the national crypto-assets implementation law, which resulted in a temporary legal gap. As a result, as of January 2026, the Polish regulator (Komisja Nadzoru Finansowego) does not yet have full formal authority to issue new CASP licenses, despite MiCA being directly applicable at the EU level.
In practice, Polish VASPs that were legally operating before the end of 2024 have been allowed to continue their activities until at least July 1, 2026, or until the adoption of a new national implementation law. At the same time, these entities cannot benefit from MiCA passporting rights and cannot provide services across the EU until they obtain CASP authorization.
Despite this transitional situation, regulatory oversight has not been suspended. Regulators may carry out audits to assess how well VASPs are preparing for MiCA standards. Here’s how it works:
- You’ll get a notice before an audit starts, and there’s a waiting period of 7 to 30 days.
- The notice will say what the audit will focus on, like checking the qualifications of board members or ensuring compliance with AML rules.
- Board members will need to show proof of their qualifications, like training certificates or at least one year of experience in virtual currency activities. A clean criminal record is also required to meet Polish AML regulations.
- If a company refuses to accept the audit, it could be removed from the VASP register.
- It’s a good idea to get your compliance documents in order ahead of time.
To smoothly transition from a VASP to a CASP, companies need to set up a solid compliance framework that meets MiCA’s rules. Here are the main things to keep in mind:
1. Capital Requirements:
MiCA sets different capital levels depending on what services you're offering:
- €50,000 for advisory services and order execution.
- €125,000 for custody services or crypto-to-fiat exchanges.
- €150,000 for running a trading platform.
CASPs must maintain the higher of the statutory minimum capital or one quarter of the previous year’s fixed overheads as a capital buffer.
2. Cash Account Requirements
CASPs must keep client funds separate from their business assets by holding them in separate cash accounts at approved banks.
3. Documentation Requirements
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has detailed guidelines on what documents you need, including:
- Program of Operations: a description of the services you provide, where you operate, your marketing approach, and financial plans.
- Governance Policies: internal controls, company structure, and compliance team roles.
- Business Continuity Plan: plans to keep operations going in case of emergency.
- AML Documentation: policies to handle money laundering and terrorism financing risks.
- Client Asset Segregation Policy: measures to protect client assets.
- Complaints-Handling Procedures: how to manage customer complaints.
Under crypto regulation, user-facing legal documents are reviewed as part of licensing, banking, and audit procedures. We advised Hasher Wallet on aligning its Terms of Use and Privacy Policy with the actual product architecture, custody model, and data flows. This alignment reduces regulatory and banking friction during licensing and ongoing supervision.
Crypto companies in Asia and Oceania
The region offers high growth potential, a well-developed financial infrastructure, strong support for innovation, and a large number of skilled professionals in blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
However, many countries still have uncertain or frequently changing regulations for cryptocurrencies, which can create significant challenges for operating a business and remaining compliant. In certain countries within the region, stringent regulatory practices and substantial financial requirements for licenses and permits can pose obstacles to market entry.
Let's take a look at the countries that our clients often inquire about: the UAE and Singapore.
UAE
When it comes to the UAE, people often mention free zones like IFZA and DSOA. This is the easiest way to enter the UAE market, but keep in mind that a company can only provide services within the free zone. So, your decision should be based on a clearly defined business plan.
The UAE imposes substantial requirements on crypto companies. The minimum required share capital ranges from approximately AED 500,000 (≈ €130,000) for payment and transfer services to AED 1,500,000 (≈ €390,000) for those seeking a cryptocurrency exchange license or custody activities. If a company provides multiple types of services, the capital must be increased for each type.
The company is required to hold reserve assets equal to the full amount of its liabilities to clients. Additionally, under the 2026 standards, companies are expected to maintain Net Liquid Assets equal to at least 1.2 times their monthly operating expenses.
The company must have at least two resident "Responsible Individuals" in the UAE, including a designated AML/Compliance Officer. VARA might require increasing the number of AML officers or management staff, such as adding a CFO in addition to the CEO.
It's mandatory to obtain professional insurance, directors & officers insurance, commercial crime/hot wallet insurance, and other insurance required by VARA. Starting in 2025, VARA also enforces a mandatory Technology & Information Rulebook, which includes independent technology audits and cybersecurity assessments.
Any crypto business in or from Dubai (except DIFC) must obtain a VARA license before starting operations. The VARA licensing process in 2026 follows a two-stage path: first, obtaining an Approval to Incorporate (ATI) for operational setup, followed by the final VASP License (Full Market Product or FMP). The preliminary MVP license stage is no longer the standard entry point for new firms.
The VARA licensing process includes several steps:
- Initial сonsultation: Contact VARA to understand the requirements and the type of license needed.
- Document submission: Prepare and submit detailed documentation, including business plans, financial reports, and compliance policies.
- Evaluation and examination: VARA will assess the application, conduct interviews, and carry out inspections.
- Approval and issuance: After approval, the license will be issued, and the company can start operating.
Singapore
Just like in the UAE, Singapore has high requirements for crypto companies. The company's structure must include at least one executive director who is ordinarily resident in Singapore, typically a Singapore citizen, permanent resident, or an Employment Pass holder. Another acceptable structure is having a non-executive director who is a Singaporean citizen and an executive director with a work permit. As in the UAE, you also need to hire a locally based AML/compliance officer.
The minimum base capital is SGD 250,000 for a Major Payment Institution (MPI) license, while a Small Payment Institution (SPI) requires SGD 100,000. You will need to prove the origin of these funds.
Key regulatory updates for 2026:
- Full enforcement of the Payment Services Act (PSA): As of mid-2025, the transitional arrangements for Digital Payment Token (DPT) service providers operating from Singapore have largely ended. Entities with a place of business in Singapore, including those serving overseas clients only, are now expected to be licensed under the PSA or to cease regulated activities.
- Customer Asset Protection: Under MAS supervisory guidance, Digital Payment Token service providers are expected to hold at least 90% of customer digital assets in cold storage. This requirement is a cornerstone for any firm operating under a crypto wallet license (officially regulated as a custodial DPT service), ensuring strict segregation of client assets.
- Retail Restrictions: Retail access to high-risk crypto products, including lending and staking, is heavily restricted, with strict conduct and suitability requirements.
To establish a crypto business in Singapore in 2026, adhere to the following steps:
- Register the company and secure a physical office.
- Write a detailed business plan, including an external auditor assessment of your technology and cybersecurity controls.
- Designate a resident director and a local AML officer.
- Lodge an application with the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and pay the application fee (approx. SGD 1,000 – 1,500).
- Appoint a Case Officer and undergo thorough due diligence.
- Verify shareholders and prove the source of wealth.
- Pass the regulator interview and receive In-Principle Approval (IPA).
- Set up a local bank account and fund it with the necessary capital and security deposit (if required).
- Complete a final technology audit to receive the final license.
Crypto companies in offshore jurisdictions
Here’s why offshore jurisdictions are attractive for crypto companies:
- Favorable regulatory environment. Offshore jurisdictions such as The Bahamas, Cayman Islands, and British Virgin Islands often provide dedicated digital asset regulatory frameworks, historically perceived as more flexible than those in major onshore markets.
- Tax advantages. Many offshore jurisdictions offer tax neutrality or significantly lower tax rates on income, profits, or capital gains. For example, the Cayman Islands impose no corporate or capital gains tax, while the British Virgin Islands offer no income tax, inheritance tax, or capital gains tax for businesses.
- Confidentiality and privacy. Many offshore jurisdictions provide limited public disclosure, although beneficial ownership transparency and AML reporting obligations have materially increased since 2024. In jurisdictions such as the British Virgin Islands, ownership information is not publicly accessible but must be disclosed to regulators and competent authorities.
- Fast and efficient incorporation. Offshore jurisdictions typically offer streamlined incorporation processes, although licensing and supervisory timelines have lengthened significantly under newer regulatory regimes.
- Reduced operational costs. In some cases, offshore jurisdictions still offer lower administrative costs, but compliance, governance, and audit expenses have increased materially since 2024, reducing the historical cost advantage for regulated crypto businesses.
While offshore jurisdictions continue to attract crypto companies, the regulatory gap between offshore and onshore markets has narrowed considerably:
- Increased scrutiny. Offshore crypto firms are now subject to enhanced scrutiny from international regulators, correspondent banks, and institutional counterparties, particularly when servicing EU, UK, or US clients.
- Reputational considerations. Operating from an offshore jurisdiction may raise additional due diligence and governance expectations, especially for companies targeting institutional capital or regulated markets.
Let’s explore The Bahamas as a jurisdiction to run a crypto startup.
Once considered one of the most flexible offshore options, The Bahamas underwent a fundamental regulatory shift with the adoption of the Digital Assets and Registered Exchanges Act, 2024 (DARE Act), which replaced the 2020 framework in its entirety.
Key changes under DARE Act 2024 include:
- A significantly stricter licensing regime, with enhanced requirements for governance, internal controls, risk management, and technology systems.
- Stablecoin regulation: The Bahamas now operates one of the strictest regulatory regimes globally for stablecoin issuers. Algorithmic stablecoins are explicitly prohibited, and asset-backed stablecoins are subject to enhanced reserve, disclosure, and supervisory requirements.
- Staking as a regulated activity: For the first time in offshore practice, staking offered as a service is expressly regulated, requiring licensing and ongoing supervision.
- Enforcement powers: Maximum administrative penalties now reach up to USD 500,000, alongside suspension or revocation of licenses.
Licensing continues to be overseen by the Securities Commission of The Bahamas, with approval timelines typically ranging from six to eighteen months, depending on the complexity of the business model.
Choosing the right country to register your crypto startup and obtain a crypto license is a critical step that directly affects regulatory risk, scalability, access to banking, and long-term business viability.
As of 2026, the EU offers a highly structured and predictable regulatory environment for starting and operating crypto businesses. Under MiCA, companies can benefit from a European-level license, allowing them to operate across the entire EU internal market under a single authorization. However, this comes with high entry thresholds, strict governance and compliance standards, and active supervisory enforcement, making the EU better suited for well-capitalized and compliance-ready teams.
Asian jurisdictions like the UAE and Singapore remain attractive but highly selective. The UAE offers opportunities in fast-growing crypto ecosystems such as Dubai, but imposes strict capital, liquidity, governance, and technology requirements. Singapore, on the other hand, provides a stable regulatory environment and strong institutional credibility, but entry barriers are high, retail activities are tightly restricted, and licensing timelines remain long and resource-intensive.
In the US, although the market is large and promising, licensing requirements and regulatory pressures continue to be significant. The split between federal and state levels creates a costly and operationally demanding environment, requiring substantial legal, compliance, and financial resources.
Offshore jurisdictions, like the Cayman Islands, The Bahamas, and the British Virgin Islands, no longer represent a “light-touch” alternative. While they provide formal regulatory frameworks for digital asset businesses, this flexibility comes with active enforcement, heightened international scrutiny, reputational considerations, and ongoing challenges in securing stable banking relationships.
When choosing a country for your crypto startup, it’s crucial to consider all these factors to ensure an effective launch and continued business growth. In 2026, there is no universally “best” jurisdiction. We recommend thoroughly analyzing not just the current conditions but also enforcement trends, supervisory practices, and the direction of regulatory change to keep your business competitive and compliant with legal standards.




